TL; DR: Ethical AI in Agile
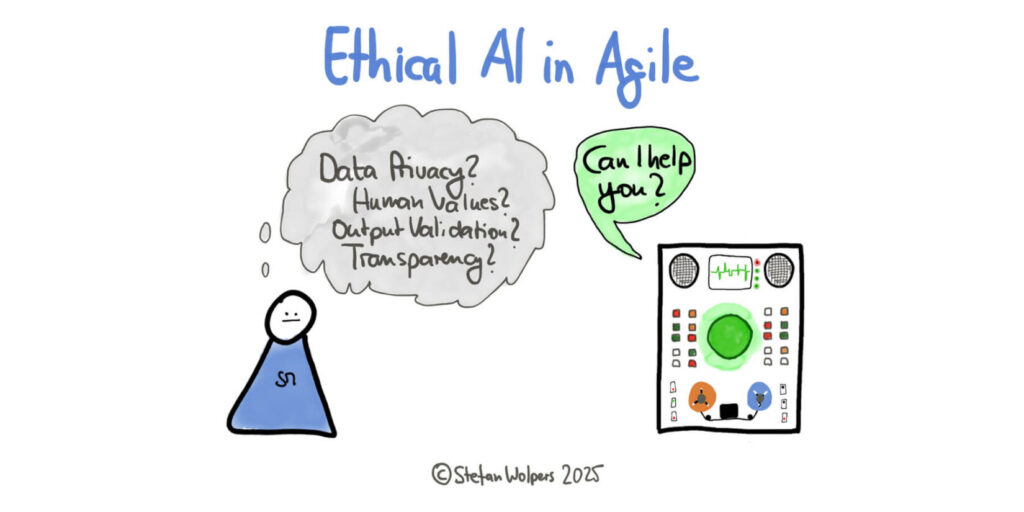
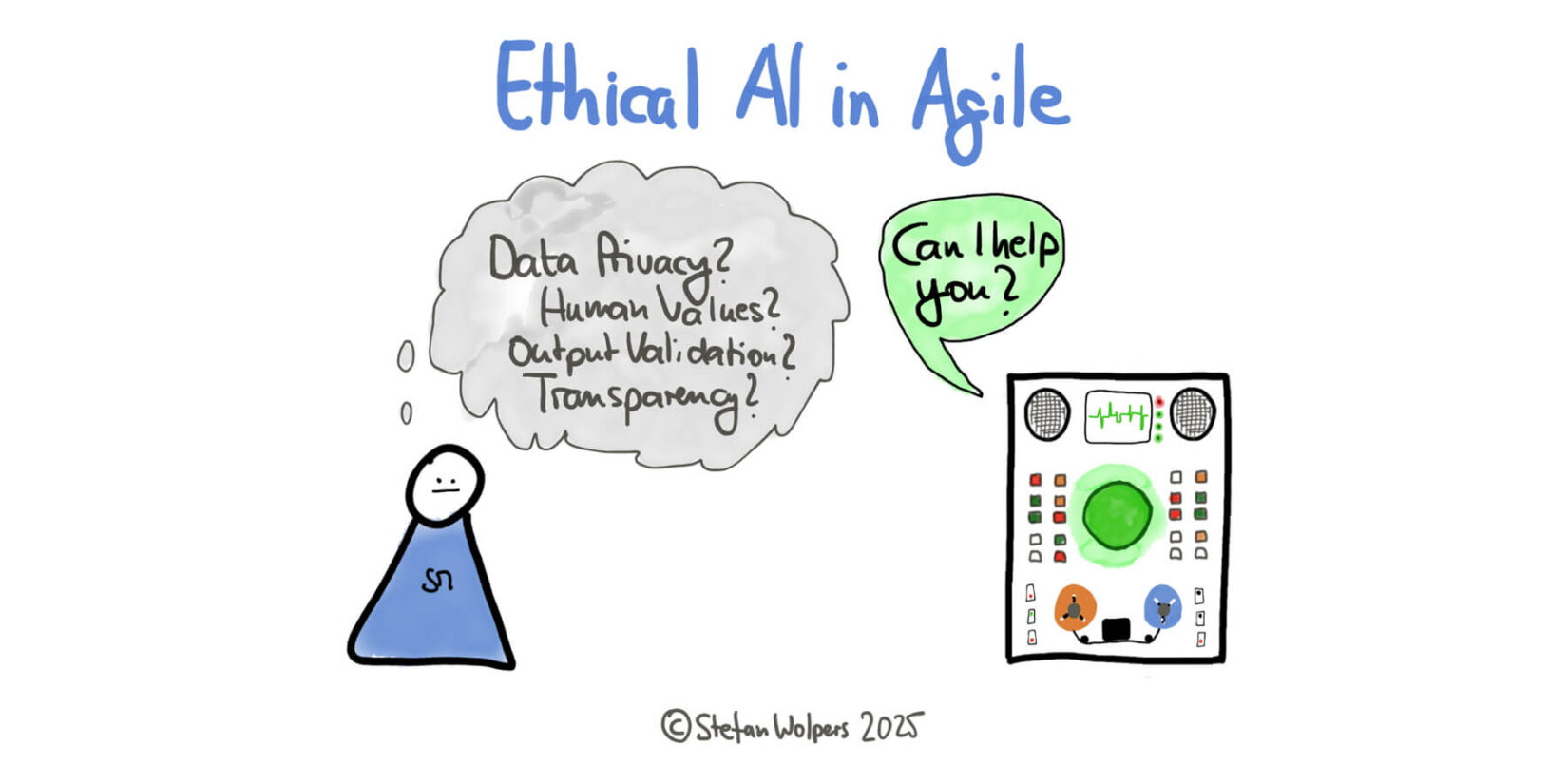
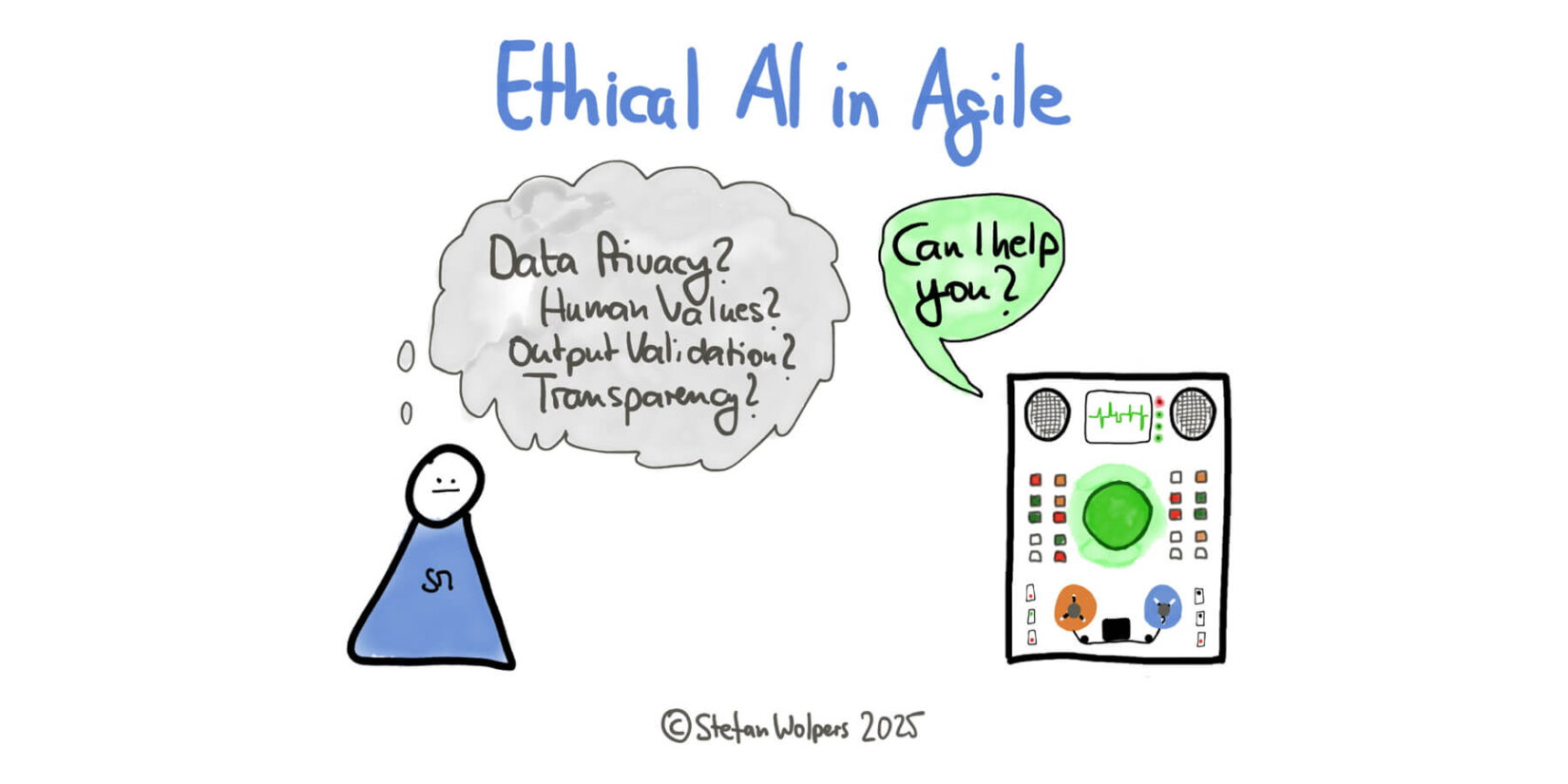
Agile teams face ethical challenges. However, there is a path to ethical AI in Agile by establishing four pragmatic guardrails: Data Privacy (information classification), Human Value Preservation (defining AI vs. human roles), Output Validation (verification protocols), and Transparent Attribution (contribution tracking).
This lightweight framework integrates with existing practices, protecting sensitive data and human expertise while enabling teams to confidently realize AI benefits without creating separate bureaucratic processes.
🇩🇪 Zur deutschsprachigen Version des Artikels: Ethische KI und Agilität: Vier Grundsätze, die jeder Scrum Master jetzt bedenken muss.
🗞 Shall I notify you about articles like this one? Awesome! You can sign up here for the ‘Food for Agile Thought’ newsletter and join 42,000-plus subscribers.
🎓 🖥 🇬🇧 The AI-Enhanced Advanced Product Backlog Management Course Version 2—June 23, 2025
Are you facing problems aligning vision, stakeholders, your team, and delivering real value?
Is your contribution as a product leader questioned?
Then, prepare to transform your career with my AI-enhanced, comprehensive, self-paced online class. Dive deep into professional Product Backlog management techniques supported by videos, exercises, and the latest AI models.
👉 Please note: The course will only be available for sign-up until June 30, 2025!
🎓 Join the Launch of the AI-Enhanced Version 2 on June 23: Learn How to Master the Most Important Artifact for any Successful Agile Practitioner!
Ethical AI in Agile Needs Scrum Masters as Guardians
Agile practitioners are deeply concerned about Ethical AI in Agile, not as distant fears but as immediate challenges. In a recent survey I conducted with agile professionals, respondents revealed widespread concerns about data privacy (“How to make sure I do not leak confidential information”), job security (“Will my dev colleagues just be AI machines? What is my job then as a Scrum master?”), and output reliability (“How can I evaluate the quality and correctness of results?”).
My survey’s open-ended question about ethical concerns in AI and Agile uncovered remarkably consistent themes. Data privacy consistently emerged as the top concern, followed by job security anxiety and questions about AI reliability. These insights directly inform the guardrails presented in this article.
Scrum Masters are uniquely positioned to address these concerns by establishing practical AI boundaries. Rather than becoming “AI police,” they can serve as ethical compasses, creating lightweight guardrails that integrate naturally with existing agile practices. These guardrails ensure AI enhances rather than undermines agile values, team effectiveness, and individual contributions.
This approach isn’t about comprehensive AI governance—it’s about the pragmatic, immediate implementation of ethical boundaries that protect what matters most: sensitive data, human expertise, and work integrity.
Cannot see the form? Please click here.
The Four Critical Guardrails for Ethical AI in Agile
1. Data Privacy & Compliance Guardrail
The Challenge: My survey data reveals this as practitioners’ #1 concern, with specific worries about protecting confidential information, GDPR, and EU AI Act compliance. As one respondent noted: “Data input usage by AI creators for machine learning, how to make sure I do not leak confidential information?”
Key Implementation Elements:
- Data classification system (Public, Internal, Confidential, Restricted),
- Clear protocols for sanitizing inputs before sharing with external AI tools,
- Compliance checklists for different regulatory environments,
- Technical approaches to minimize data exposure.
Why It Matters: Ignoring this guardrail exposes the organization to significant legal, financial, and reputational damage, directly contravening Agile’s emphasis on trust and value delivery.
Practical Implementation Approach: Create a simple red/yellow/green classification system:
- Green: General agile practices, non-proprietary knowledge,
- Yellow: Anonymized project elements requiring leader review,
- Red: Confidential data never to be shared with external AI.
Example in Action: A Scrum team creates a “data sensitivity categorization system” for product and project information. User story templates were classified as “public” (shareable with AI), specific feature descriptions as “internal” (requiring anonymization), and customer data as “restricted” (never shared). This system is embedded in their Definition of Done, requiring explicit verification that no restricted data was exposed during AI interactions.
2. Human Value Preservation Guardrail
The Challenge: Survey respondents expressed significant anxiety about AI replacing their roles: “Do we need an SM as we can just use ChatGPT” and “How do we use AI to help ‘AI-proof’ our jobs from elimination?”
Key Implementation Elements:
- Clear delineation between AI-appropriate and human-essential activities,
- Protocols that position AI as enhancing rather than replacing practitioners,
- Identification of uniquely human elements of agile roles,
- Team agreements about when human judgment takes precedence.
Why It Matters: Without this guardrail, teams risk over-delegating to AI, diminishing the human elements that make Agile effective, and creating anxiety that reduces engagement and creativity.
Practical Implementation Approach: Create a “human-AI partnership framework” that explicitly identifies:
- AI-Optimal Tasks: Routine documentation, initial draft creation, pattern recognition,
- Human-Optimal Areas: Stakeholder relationship building, conflict resolution, values-based decisions,
- Partnership Activities: Areas where human direction and AI assistance create the best results.
Example in Action: A product team experiences anxiety about AI replacing team members and creates a “human-AI partnership framework” visualized as a spectrum. For example, AI might help generate initial user story drafts, but humans would lead stakeholder conversations to uncover needs. Implementing this framework may lead to team members feeling more secure about their unique contributions and more strategic about when to leverage AI assistance.
3. Output Validation Guardrail
The Challenge: Practitioners in my survey expressed significant concerns about AI reliability, noting “simply wrong responses” and asking, “at what point can you feel like AI output is reliable?”
Key Implementation Elements:
- Verification protocols for different types of AI outputs,
- Team practices for critical assessment of AI-generated content,
- Systems to track and improve AI reliability over time,
- Procedures for handling identified AI errors or hallucinations.
Why It Matters: Without systematic validation, teams risk implementing incorrect solutions, making decisions based on false information, and gradually losing trust in both AI and human oversight.
Practical Implementation Approach: Implement a “triangulation protocol” requiring:
- Independent verification from existing documentation or team knowledge,
- Clear marking of AI-generated content until verified,
- Tracking of reliability patterns to identify high-risk vs. low-risk use cases.
Example in Action: Developers require technical recommendations by AI to be verified against either existing documentation or a second team member’s confirmation. The team maintains a simple log of verification results, allowing them to identify which tasks are most appropriate for AI assistance. This approach has the potential to catch potential issues before implementation while still allowing the team to benefit from AI’s strengths.
4. Transparent Attribution Guardrail
The Challenge: Survey respondents raised concerns about intellectual property and disclosure, questioning “How to protect your company’s IP from being learned from” and whether “everyone should know when AI is involved in the loop.”
Key Implementation Elements:
- Clear disclosure standards for AI-generated content,
- Intellectual property protection protocols,
- Methods to maintain authenticity in AI-augmented communication,
- Documentation of AI contribution to work products.
Why It Matters: Without transparency, teams risk intellectual property disputes, erosion of stakeholder trust, and loss of authentic human voice in communications—all core elements of Agile’s emphasis on transparency and trust.
Practical Implementation Approach: Create an “AI contribution registry” documenting:
- Which elements were AI-generated vs. human-created,
- What source material was provided to the AI,
- How AI suggestions were modified before implementation,
- Appropriate attribution in final deliverables.
Example in Action: UX designers may use AI for design ideation to create a simple “contribution registry” documenting the provenance of different elements. If AI generates more than 50% of the content for customer-facing materials, they disclose it to stakeholders. For internal content, they maintained records of which components were AI-assisted in their design system. This practice helps them to maintain stakeholder trust while ensuring appropriate attribution. When a stakeholder questions a particular design approach, the team can immediately clarify which aspects were human-directed versus AI-suggested, building credibility.
Implementing Ethical AI in Agile in Regulated Environments
My survey respondents specifically highlighted challenges in governmental and regulated contexts, noting “Limitations of use in governmental context” and “unsure if I’m allowed to use AI for my work at a government agency.”
For Teams with Strict Prohibitions
- Identify AI tools approved for organizational use,
- Create clear guidance on information that cannot be shared,
- Explore on-premises or private cloud solutions where appropriate,
- Develop fallback processes for scenarios where AI cannot be used.
For Teams with Evolving Policies
- Document assumptions and decisions about AI use,
- Implement stringent verification protocols,
- Create transparency with compliance stakeholders,
- Regularly review practices as organizational policies evolve.
Key Questions for Regulated Environments
- What specific regulations govern our data and AI use?
- Which AI tools are approved for organizational use?
- What verification is required before implementing AI suggestions?
- Who needs to be informed about AI use in our deliverables?
- What documentation must we maintain about AI interactions?
Practical Next Steps for Ethical AI in Agile: Getting Started with Guardrails
Begin implementing ethical guardrails with these focused activities to avoid AI usage from becoming opportunistic and getting out of hand quickly:
0. Team Buy-in and Context Setting (30 minutes)
- Share survey findings about practitioner concerns,
- Discuss specific team worries about AI ethics,
- Establish a shared understanding of ethical guardrail benefits,
- Gain commitment to initial implementation.
1. Data Classification Workshop (Initial session: 1-2 hours)
- Identify types of information your team works with,
- Create simple categories (public, internal, confidential, restricted),
- Define clear rules for what can be shared with AI tools,
- Document in a visible, accessible format.
2. Human-AI Partnership Mapping (Initial session: 1-2 hours)
- Identify team activities that benefit from AI assistance,
- Clarify which aspects must remain primarily human-driven,
- Create a visual spectrum of appropriate AI involvement,
- Discuss anxieties and address concerns openly.
3. Verification Protocol Design (Initial session: 1 hour, with refinement)
- Define verification requirements for different AI outputs,
- Create simple checklists for common AI use cases,
- Establish tracking for reliability patterns,
- Integrate into the Definition of Done.
4. Adding AI to Your Working Agreement (Initial session: 1-2 hours)
- Draft guidelines for when and how AI should be used,
- Define disclosure requirements for AI-generated content,
- Clarify how AI contributions should be documented,
- Establish an escalation path for ethical concerns.
5. Retrospective Integration (15-30 minutes)
- Add “Ethical AI Use” as a regular Retrospective topic,
- Create simple prompts to evaluate guardrail effectiveness,
- Celebrate successful ethical AI practices,
- Continuously improve based on team experience.
The Benefits of Ethical AI Guardrails
Implementing these Ethical AI in Agile guardrails delivers significant benefits:
For Scrum Masters and Agile Coaches, they represent an opportunity for substantial role enhancement, positioning you as a forward-thinking leader in AI adoption within your organization. You’ll develop specialized expertise in ethical AI implementation that is increasingly valued by organizations navigating digital transformation. This proactive approach to Ethical AI in Agile helps you mitigate risks by preventing issues before they damage the team’s reputation or create regulatory concerns. Perhaps most importantly, you’ll gain greater confidence in navigating ambiguous situations with clear ethical guidelines, transforming uncertainty into structured decision-making.
For agile Teams, implementing ethical guardrails creates psychological safety by establishing clarity about appropriate AI use in different contexts. This approach promotes balanced adoption, preventing over-reliance on AI for decisions requiring human judgment and under-utilizing AI where it could provide significant value. Teams develop consistent practices across members, establishing a shared understanding that reduces confusion and improves coordination. The guardrails enable innovation within boundaries, allowing teams to experiment creatively with AI while maintaining the ethical foundations that protect team members, customers, and the organization.
For Organizations, Ethical AI in Agile guardrails provide substantial risk reduction by mitigating legal, reputational, and operational risks associated with unchecked AI adoption. They ensure cultural alignment by connecting AI implementation directly to organizational values and principles. These frameworks position the organization for regulatory readiness, staying ahead of emerging AI regulations rather than scrambling to comply retroactively. Perhaps most critically, ethical guardrails maintain customer trust by preserving the integrity of products and services, ensuring that AI enhances rather than compromises the organization’s commitment to its customers.
Mitigating Common Resistance Points
You may encounter these objections when implementing ethical guardrails:
“This will slow us down with bureaucracy:” Start with minimal viable guardrails focused on the highest risk areas and demonstrate value through risk prevention and efficiency.
“AI ethics is too abstract and philosophical:” Focus on concrete, practical guidelines relevant to daily work. Connect to existing team values and principles.
“This isn’t the Scrum Master’s domain:” Connect to core Scrum Master responsibilities of process health and impediment prevention, positioning it as an enhancement of the existing role.
“We’re too small/early to worry about Ethical AI in Agile:” Demonstrate how early ethical guidance prevents rework and reputation damage. Start with a lightweight implementation.
“The AI tools already handle ethics:” Illustrate gaps in commercial AI tools’ ethical safeguards. Show examples of potential issues specific to your context.
Contextual Integration: A Complementary Approach
For teams seeking to deepen their ethical AI practices, “Contextual AI Integration” offers a complementary framework that naturally reinforces these guardrails. It:
- Provides minimal necessary context for specific tasks, reducing data exposure risk,
- Creates clear situational framing for AI use, preserving human judgment,
- Connects AI to existing artifacts like Definition of Done, embedding ethical considerations,
- Establishes AI Working Agreements that can incorporate ethical boundaries.
Conclusion: From Tools to Ethical Partners
The path to effective AI integration for agile teams requires deliberate, ethically bound practices that respect AI limitations and agile values.
By implementing these four guardrails, Data Privacy & Compliance, Human Value Preservation, Output Validation, and Transparent Attribution, Scrum Masters ensure AI enhances rather than undermines the human excellence at the heart of agile.
As one respondent in my survey asked: “How do we ensure AI is reflective of our thoughts and values?” These ethical guardrails provide a practical answer, not through abstract principles but through concrete practices embedded in daily agile work.
Start today. Pick one high-risk area or one concerned team member, and begin the conversation. Your first step might be scheduling the “Data Classification Workshop” outlined above. The Scrum Master who establishes these guardrails becomes not just a process facilitator but an ethical compass, helping their team navigate the complex terrain of AI-enhanced agile with integrity, confidence, and purpose.
Ethical AI in Agile — Recommended Reading
Contextual AI Integration for Agile Product Teams
AI in Agile Product Teams: Insights from Deep Research and What It Means for Your Practice
Is Vibe Coding Agile or Merely a Hype?
How to Use AI to Analyze Interviews from Teammates, Stakeholders, and the Management
The Agile Prompt Engineering Framework
The Fantastic Optimus Alpha Approach to Data-Informed Retrospectives
👆 Stefan Wolpers: The Scrum Anti-Patterns Guide (Amazon advertisement.)
📅 Scrum Training Classes, Workshops, and Events
Learn more about Ethical AI in Agile with our Scrum training classes, workshops, and events. You can secure your seat directly by following the corresponding link in the table below:
| Date | Class and Language | City | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🖥 💯 🇬🇧 May 14-June 11, 2025 | SOLD OUT: AI for Agile Practitioners: Pilot Cohort Program (English; Live Virtual Class) | Live Virtual Cohort | €199 incl. 19% VAT |
| 🖥 🇬🇧 May 26-27, 2025 | Professional Scrum Master Advanced Training (PSM II; English; Live Virtual Class) | Live Virtual Class | €1.299 incl. 19% VAT |
| 🖥 💯 🇬🇧 June 5-July 3, 2025 | SOLD OUT: AI for Agile Practitioners: Pilot Cohort Program (English; Live Virtual Class) | Live Virtual Cohort | €249 incl. 19% VAT |
| 🖥 🇩🇪 July 8-9, 2025 | Professional Scrum Product Owner Training (PSPO I; German; Live Virtual Class) | Live Virtual Class | €1.299 incl. 19% VAT |
| 🖥 🇬🇧 July 10, 2025 | Professional Scrum Facilitation Skills Training (PSFS; English; Live Virtual Class) | Live Virtual Class | €599 incl. 19% VAT |
| 🖥 💯 🇬🇧 September 4-25, 2025 | GUARANTEED: AI for Agile BootCamp Cohort #1 (English; Live Virtual Cojort) | Live Virtual Cohort | €249 incl. 19% VAT |
See all upcoming classes here.
You can book your seat for the training directly by following the corresponding links to the ticket shop. If the procurement process of your organization requires a different purchasing process, please contact Berlin Product People GmbH directly.
✋ Do Not Miss Out and Learn more about Ethical AI in Agile — Join the 20,000-plus Strong ‘Hands-on Agile’ Slack Community
I invite you to join the “Hands-on Agile” Slack Community and enjoy the benefits of a fast-growing, vibrant community of agile practitioners from around the world.
If you would like to join all you have to do now is provide your credentials via this Google form, and I will sign you up. By the way, it’s free.
The post Ethical AI in Agile: Four Guardrails Every Scrum Master Needs to Establish Now appeared first on Age-of-Product.com.